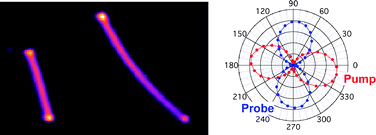
Transient absorption experiments with diffraction-limited spatial resolution have been used to study the optical absorption properties and dynamics of isolated, single silver nanowires. The images and polarization analysis show that the near-IR pump and near-UV probe beams couple to fundamentally different electron motions. The near-IR pump laser excites the propagating surface plasmon polariton (SPP) modes of the wires when focused at the ends, and multipolar plasmon modes (antenna modes) for medial excitation. The images show that these two modes have comparable optical absorption cross-sections. In contrast, the near-UV probe couples to the transverse plasmon resonance of the wire independent of the spatial position. For either end-on or medial excitation, pump laser absorption causes lattice heating and coherently excites the breathing vibrational mode of the nanowires. The vibrational quality factors depend on the acoustic impedance mismatch between the nanowire and the environment, and are similar to those recently measured for silver nanocubes. Experiments performed with spatially separated pump and probe beams, with the pump beam focused at one end to excite the propagating SPP modes, show that the amplitudes of the initial transient absorption signal and the breathing motion decrease with distance along the wire. This arises because the propagating SPP mode decays as it moves down the wire, which reduces the number of electronic excitations and, therefore, the signal level in the experiments. The measured length scale for the SPP decay is similar to that obtained in previous light scattering experiments.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...