Enzymatic activity of surface-immobilized horseradish peroxidase confined to micrometer- to nanometer-scale structures in nanocapillary array membranes†
Abstract
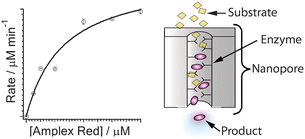
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was immobilized on the planar surfaces and inside the cylindrical nanopores of nanocapillary array membranes (NCAMs) to study how the enzyme-catalyzed oxidation of a fluorigenic substrate, Amplex Red (AR), to fluorescent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...