Neutrophil migration assay from a drop of blood†
Abstract
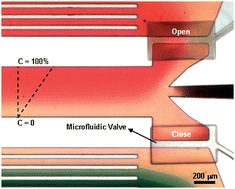
Neutrophil directional migration in response to chemical gradients, also known as chemotaxis, is one of the key phenomena in the immune responses against bacterial infection. To better study neutrophils chemotaxis, several in vitro assays have been developed that replicate chemotactic gradients around neutrophils isolated from whole blood. One drawback for most of these assays is the lengthy processing of blood required for neutrophils isolation, which can alter the responsiveness of neutrophils compared to the in vivo conditions. To address this limitation, we have designed a microfluidic chip for chemotaxis studies which can use neutrophils isolated on the chip, directly from whole blood. We have tested three different cell adhesion molecules as substrates for neutrophil isolation (P-selectin, E-selectin and fibronectin) and found average capture efficiencies of 20–40 neutrophils/mm2 at optimized concentrations. Subsequent analysis of neutrophil migration in chemoattractant gradients of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Microfluidics and point-of-care testing

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...