Continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels using dean flows and differential migration
Abstract
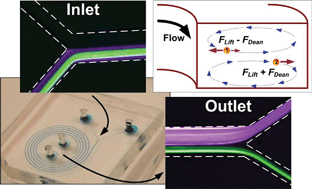
Microparticle separation and concentration based on size has become indispensable in many biomedical and environmental applications. In this paper we describe a passive microfluidic device with spiral microchannel geometry for complete separation of particles. The design takes advantage of the inertial lift and viscous drag forces acting on particles of various sizes to achieve differential migration, and hence separation, of microparticles. The dominant inertial forces and the Dean rotation force due to the spiral microchannel geometry cause the larger particles to occupy a single equilibrium position near the inner microchannel wall. The smaller particles migrate to the outer half of the channel under the influence of Dean forces resulting in the formation of two distinct particle streams which are collected in two separate outputs. This is the first demonstration that takes advantage of the dual role of Dean forces for focusing larger particles in a single equilibrium position and transposing the smaller particles from the inner half to the outer half of the microchannel cross-section. The 5-loop spiral microchannel 100 μm wide and 50 μm high was used to successfully demonstrate a complete separation of 7.32 μm and 1.9 μm particles at Dean number De = 0.47. Analytical analysis supporting the experiments and models is also presented. The simple planar structure of the separator offers simple fabrication and makes it ideal for integration with on-chip microfluidic systems, such as micro total analysis systems (μTAS) or lab-on-a-chip (LOC) for continuous

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...