Preparation of stable foams using sterically stabilized pH-responsive latexes synthesized by emulsion polymerization
Abstract
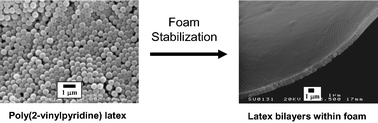
Three near-monodisperse poly(2-vinylpyridine) (P2VP) latexes of 380 nm, 640 nm and 820 nm diameter were prepared in turn by emulsion

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...