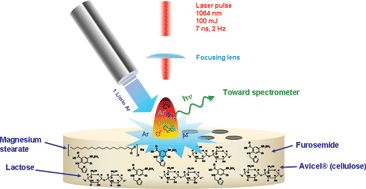
The present work describes the first quantitative molecular prediction using laser-induced molecular bands along with chemometrics. In addition, this spectroscopic procedure has demonstrated the first complete quantitative analysis utilizing traditionally insensitive elements for pharmaceutical formulations. Atomic LIBS requires certain sensitive elements, such as Cl, F, Br, S and P, in order to quantitate a specific organic compound in a complex matrix. Molecular LIBS has been demonstrated to be the first successful approach using atomic spectroscopy to evaluate a complex organic matrix. This procedure is also the first quantitative analysis using laser-induced molecular bands and chemometrics. We have successfully applied chemometrics to predict the formulation excipients and active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in a complex pharmaceutical formulation. Using such an approach, we demonstrate that the accuracy for the API and a formulation lubricant, magnesium stearate, have less than 4% relative bias. The other formulation excipients such as Avicel® and lactose have been accurately predicted to have less than a 15% relative bias. Molecular LIBS and chemometrics have provided a novel approach for the quantitative analysis of several molecules that was not technically possible with the traditional atomic LIBS procedure, that required sensitive elements to be present in both API and formulation excipients.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...