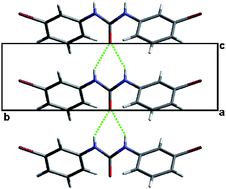
The solid state structures of a family of 1,3-bis(m-di-X-phenyl)ureas where X = Cl, Br, I and their mono- and di-tolyl analogues were determined. Crystal growth from a variety of solutions yielded isostructural and isomorphous P21212 phases for all compounds. The molecules associate into infinite [R12(6)] hydrogen bonded urea chains which are reinforced through π–π stacking interactions of neighboring phenyl rings within the chain. Short halogen–halogen contacts between anti-parallel urea chains are also observed. Ab initio calculations indicate that the rotational barrier about the amide bond is small, and that the molecular conformations observed in the crystal structures are close in energy to the calculated minima. These calculations suggest that a variety of low energy geometric conformations may be present in solution. Using a small scale conventional polymorph screening protocol (∼9 crystallization solvents and combinations thereof), analysis of the phase purity of powders obtained from a variety of solutions revealed the orthorhombic phase to be the predominant form for all compounds in all solvents. However, additional peaks were observed in select powder X-ray diffraction patterns, leaving open the possibility that concomitant polymorphism or solvate formation occurs for some compounds under particular crystallization conditions.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...