μ-Hotplate enhanced optical heating by infrared light for single cell treatment
Abstract
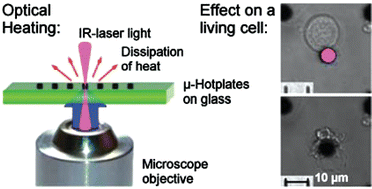
In this study we present a simple approach for fast and localised heating that relies on the strong absorbance of infrared light by microsized patterned surfaces (“μ-hotplates”). Two different materials, μ-arrays of carbon and gold, were tested with respect to their absorbance of the 830 nm diode laser light and their applicability. Both materials were found to be suitable for inducing controlled heating to a temperature increase of more than 10 °C within less than a second. The effect of optical heating on living cells (colon cancer cell line SW 480) was investigated with a modified fluorescence microscope. The temperature was controlled by varying the intensity and the exposure time of the laser light. Depending on temperature, induced death of cells in direct contact with the absorbent material was observed, or otherwise cells were kept alive. Cells survive the direct exposure of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...