A simple procedure for the photoregulation of chymotrypsin activity
Abstract
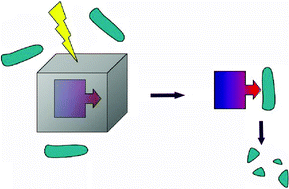
A convenient and rapid method for the photo-regulation of the proteolytic enzyme α-chymotrypsin is described. When α-chymotrypsin is coated with photolytic 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethanol residues this not only markedly reduces the capability of the enzyme to digest both of the small substrates

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...