Carbon dioxide and related heterocumulenes at zinc and lithium cations: bioinspired reactions and principles†‡
Abstract
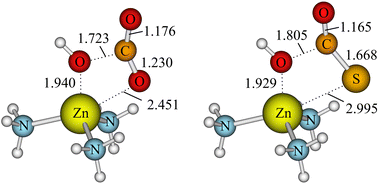
This Perspective starts with the discussion of the properties of an interesting metalloenzyme (carbonic anhydrase, CA) that performs extremely successfully the activation of carbon dioxide. Conclusions from that are important for many synthetic procedures and include experimental and theoretical investigation (DFT calculations) of such metal mediated processes in the condensed and in the gas phase in which the zinc cation plays a dominant role. This is extended to the bio-analogue activation of further heterocumulenes such as COS, an important atmospheric trace gas, and CS2. Novel metal complexes which serve as useful catalysts for the reactions (copolymerisations and cyclisation) of CO2 and oxiranes are discussed subject to the inclusion of recently published DFT calculations. We continue with the discussion of the very general aspect of the insertion of CO2 into metal–nitrogen bonds (formation of carbamates). This again is closely related to many biological or bio-analogue processes. We describe the synthesis and mechanistic aspects of characteristic metal carbamates of a wide variety of metals and include a discussion of the mechanistic aspects, especially for the formation of Mg2+ and Li+ carbamates and the formation of related cyclic products after addition of the heterocumulenes CO2, Ph-NCO or CS2 to novel ligands, the 4H-pyridin-1-ides which finally result in the formation of e.g. 1,3-thiazole-5(2H)-thiones.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Carbon dioxide at metal centres

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...