Pore structure in supermacroporous polyacrylamide based cryogels
Abstract
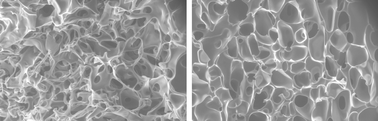
Pore size and thickness of pore walls in macroporous polyacrylamide gels, so-called cryogels (pAAm-cryogels), were controlled by varying the content of monomers in the initial reaction mixture and the cross-linker used. The thickness of pore walls in pAAm-cryogels increased with increasing concentration of monomers in the initial reaction mixture. Pore volume in the supermacroporous pAAm-cryogels was in the range of 70–93% and decreased with increasing concentration of monomers in the reaction feed. The porous structure of the pAAm-cryogels was visualized using environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) that allowed monitoring of the dehydration process in pAAm-cryogels. The accessibility of ligands covalently coupled to the polymer backbone for low molecular weight target, Cu(II) ions, and high molecular weight target, the protein lysozyme, was assessed for pAAm-cryogels produced from feeds with different monomer concentration. The amount of bound Cu(II) ions increased linearly with increasing monomer concentration in the reaction feed, suggesting that all ligands are equally accessible for small targets. On the contrary, lysozyme binding demonstrated a clear maximum at monomer concentration about 18% suggesting that only ligands present at the surface of pore walls are accessible for high molecular weight targets.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...