Liquid crystal elastomers, networks and gels: advanced smart materials
Abstract
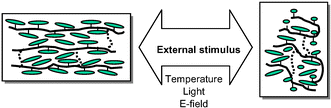
The principal concepts, preparation methods, important features of liquid crystal elastomers, anisotropic networks and gels, as well as recent exciting progress in this field are reviewed. Discussions are focused on their potential applications as smart materials for converting electrical or optical energy into mechanical energy and vice versa – such applications include artificial muscles, light scattering electro-optical switches and display materials, electro- or photo-controllable micro- or nano-machinery, electrically switchable color-tunable reflectors (mirrors) and full-color reflective display, fine-tunable and low-threshold mirror-less lasing, etc. In addition, some innovative anisotropic networks consisting of ferroelectric liquid crystals, discotic mesogens and mesomorphic ladder-like polysiloxanes are also highlighted.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...