Dioxygen reduction by multi-copper oxidases; a structural perspective†
Abstract
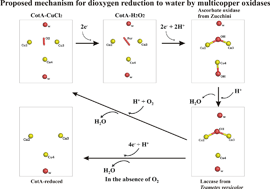
The multi-copper oxidases oxidise substrate molecules by accepting electrons at a mononuclear copper centre and transferring them to a trinuclear centre. Dioxygen binds to the trinuclear centre and, following the transfer of four electrons, is reduced to two molecules of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...