Aldehyde detection by chromogenic/fluorogenic oxime bond fragmentation†
Abstract
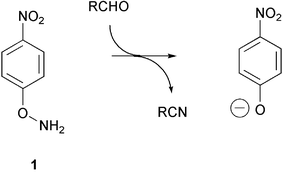
Amination of 4-nitrophenol, umbelliferone and 4-methylumbelliferone gave the corresponding oxyamines 1–3. These oxyamines react with aldehydes and ketones to form oximes. In the case of aliphatic aldehydes and electron-poor aromatic aldehydes, the oximes undergo base-catalyzed fragmentation in aqueous buffer in the presence of bovine serum albumin to give the parent phenols, which is the acyclic analog of Kemp's elimination reaction of 5-nitrobenzisoxazole 28. The process can be used as a spectrophotometric assay for formaldehyde under aqueous neutral conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...