Kinetic evidence that cysteine reacts with dopaminoquinone via reversible adduct formation to yield 5-cysteinyl-dopamine: an important precursor of neuromelanin
Abstract
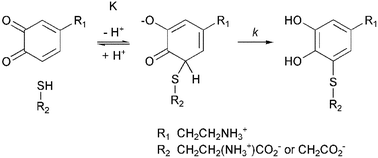
The reaction of cysteine (cys) with dopaminoquinone (DQ) to form (mainly) 5-cysteinyl-dopamine (5-cys-DA) is of interest because it is known to play a role in the production of melanin in the mammalian brain. To gain insight into this important reaction, an in vitro detailed kinetic study was undertaken. It has been established that cys reacts with DQ via the initial reversible formation of an intermediate adduct or complex and that this adduct then decomposes to form 5-cys-DA. A little 2-cys-DA, is almost certainly formed at the same time but its presence could not be kinetically investigated. Clarification of the kinetic data was aided by following the reaction of DQ with a cys analogue, mercaptoacetic acid (maa). Maa was found to react in a similar fashion, but also forms, reversibly, a bis-complex. This bis-complex, 2,5-(maa)2-dopaminoquinone, is in equilibrium with the di-protonated compound but neither of these species reacts further over the timescale employed in these kinetic studies. Equilibrium constants and first-order rate constants have been extracted from the data and the cys complex is found to be weaker than its maa analogue by an order of magnitude (Kcys = (1.09 ± 0.02) × 10−3; K1,maa = (7.45 ± 0.11) × 10−3). (Note that the possibility that cys also forms a bis-complex at much higher cys concentrations cannot be excluded.) The rates of decomposition differ markedly—the cys complex has the value kcys = 1830 ± 50 s−1 whereas the rate constant for the decomposition of the maa complex is kmaa = 69.3 ± 0.02 s−1 and we attribute this difference to the effect of the positive charge carried by the amino-group on cys. Finally, the constants obtained are used to compare the reactivity of thiol addition with ring cyclization (U. El-Ayaan, E. Herlinger, R. F. Jameson, and W. Linert, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 1997, 2813–2818) and we show how this has important implications concerning the production of neuromelanin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...