Electrochemical fabrication of single-walled carbon nanotubes–DNA complexes by poly(ethylenedioxythiophene) and photocurrent generation by excitation of an intercalated chromophore†
Abstract
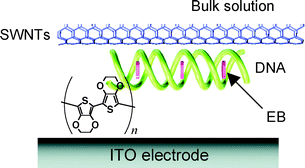
It was found that single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) solubilized into water by complexation with DNA (salmon testes) can be readily deposited on the ITO electrode by electrochemical oxidative polymerization of ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT). The driving force for this novel deposition is an electrostatic interaction between the anionic charges of wrapping DNA and the cationic charges of poly(EDOT) formed in the oxidative polymerization process. The presence of poly(EDOT), SWNTs and DNA in the composite was confirmed by measurements of UV-Vis, IR, resonance Raman spectra, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The composite adsorbed a DNA intercalator (ethidium bromide: EB) very efficiently, which is regarded to be further evidence for inclusion of DNA. The surface morphology, characterized by CLSM, SEM and AFM, featured the network structure consisting of 0.5–ca. 10 µm nanorods. Very interestingly, we found that photoexcitation of EB bound to the DNA generates the photocurrent, indicating that the excited energy of EB is injected into SWNTs, which is collected by the electroconductive poly(EDOT) film on the ITO electrode. We believe, therefore, that the present system is a very convenient method to explore new materials related to redox and photochemical functions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...