The thermal decomposition of 5-membered rings: a laser pyrolysis study
Abstract
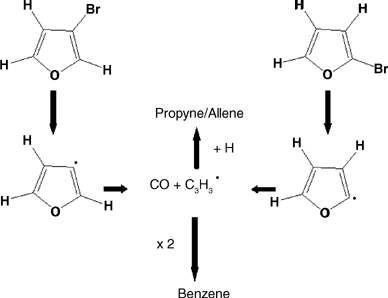
The mechanisms of pyrolysis of cyclopentadiene, furan, pyrrole and thiophene have been investigated using a combination of IR laser powered homogeneous pyrolysis, chemical and physical trapping of radical intermediates, and use of precursors specifically designed to generate selected radical intermediates. The results confirm the central role played by free radicals in the cases of cyclopentadiene and thiophene, and the dominant step of 1,2-H shifts in the cases of furan and pyrrole. The experimental results may be interpreted according to the high level ab initio calculations recently reported in the literature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...