Influence of heteroligands on the composition, structure and properties of homo- and heterometallic zirconium alkoxides. Decisive role of thermodynamic factors in their self-assembly†‡
Abstract
Interaction of the commercial “Zr(OnPr)4” with an excess of iPrOH provides in high yields a new solid crystalline but highly soluble precursor Zr2(μ-OnPr)2(OiPr)6(iPrOH)2 (2). Interaction of 1 eq. of 2 with 1 eq. of Co(acac)2 results in quantitative transformation into a mixture of Co2Zr2(OnPr)4(OiPr)6(acac)2 (3), with a structure representing a fragment of hexagonal packing of metal atoms and alkoxide ligands (typical for derivatives of primary alcohols), and Zr2(OiPr)6(acac)2 (4). Reaction of 1 eq. of homoleptic zirconium isopropoxide, Zr2(OiPr)8(iPrOH)2 (1), with 1 eq. of Co(acac)2 provides a new complex CoZr2(OiPr)8(acac)2 (5) having a linear chain structure (characteristic of sec-alcohol derivatives) in quantitative yield. Microhydrolysis of a mixture of 1.5 eq. of 2 and 1 eq. of Co(acac)2 gave in moderate yield CoZr3O(OnPr)3(OiPr)5(acac)4 (6), with a tetrahedral CoZr3O core characteristic of zirconium sec-oxoalkoxides. Modification of a solution of barium and zirconium isopropoxides in toluene (Ba∶Zr = 1∶1) with 1.5 eq. of Hacac results almost quantitatively in a mixture of insoluble Ba(acac)2 and soluble and volatile heterometallic alkoxide Ba2Zr4(OiPr)18(acac)2 (7). Addition of 2 eq. of Hthd to a mixture of barium and zirconium n-propoxides in toluene (Ba∶Zr = 1∶1) gives highly soluble and volatile complex Ba2Zr2(thd)4(OnPr)8(nPrOH)2 (8). Reaction of the in situ obtained Ba(thd)2 with 0.5 eq. of 2 provided almost quantitatively another highly soluble and volatile precursor Ba2Zr2(thd)4(OnPr)2(OiPr)6 (9). Addition of 2 eq. of Hthd to a mixture of strontium and zirconium isopropoxides in toluene (Sr∶Zr = 1∶1) gives highly soluble complex Sr2Zr2(thd)4(OiPr)8 (10) volatilized on heating via complete decomposition into Sr(thd)2, Zr(thd)2(OiPr)2 and non-volatile products. Bimetallic hydroxo-isopropoxides of strontium and barium, Sr2Zr2(OH)2(OiPr)10(iPrOH)4 (11) and Ba2Zr2(OH)2(OiPr)10(iPrOH)6 (12), have been obtained in good yields via microhydrolysis of solutions of isopropoxides in toluene/isopropanol media. All compounds have been characterized by a variety of spectroscopic techniques, and compounds 1–9 and 11–12 also by X-ray single crystal studies. The principles in construction of zirconium alkoxides – products of thermodynamically controlled molecular self-assembly – and their stability and reactivity are discussed in connection with the sterical role played by the chosen ligands.
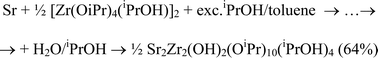
- This article is part of the themed collection: From Molecules to Materials: Materials Discussion 7

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...