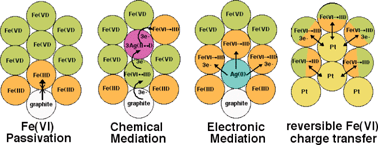
This study addresses a fundamental challenge posed by hexavalent iron electrochemical irreversibility, which had slowed practical development of reversible Fe(VI) cathodes; nanolayers circumvent fundamental passivation challenges, and are electrodeposited from solution phase FeO42−, forming 601 mAh g−1 Li, and 485 mAh g−1 Na, Fe(III/VI) alkaline cathodes, the latter exhibiting 100–200 storage cycles at 80% depth of discharge, providing pathways towards metal hydride batteries with twice the cathode capacity.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...