Health effects from stratospheric ozone depletion and interactions with climate change†
Abstract
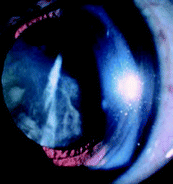
The potential health effects of elevated levels of ambient UV-B radiation are diverse, and it is difficult to quantify the risks, especially as they are likely to be considerably modified by human behaviour. Nevertheless epidemiological and experimental studies have confirmed that UV radiation is a definite risk factor for certain types of cataract, with peak efficacy in the UV-B waveband. The causal link between squamous cell carcinoma and cumulative solar UV exposure has been well established. New findings regarding the genetic basis of skin cancer, including studies on genetically modified mice, have confirmed the epidemiological evidence that UV radiation contributes to the formation of basal cell carcinomas and cutaneous melanomas. For the latter, animal models have demonstrated that UV exposure at a very young age is more detrimental than exposure in adulthood. Although suppression of certain immune responses has been recognised following UV exposure, the impact of this suppression on the control of infectious and autoimmune diseases is largely unknown. However, studies on several microbial infections have indicated significant consequences in terms of symptoms or reactivation of disease. The possibility that the immune response to vaccination could be depressed by UV-B exposure is of considerable concern. Newly emerging possibilities regarding interactions between ozone depletion and global climate change further complicate the risk assessments for human health but might result in an increased incidence of cataracts and skin cancer, plus alterations in the patterns of certain categories of infectious and other diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...