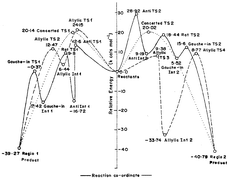
Structures and energetics of reactants, transition structures, diradical intermediates and products of the 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of allene with diazomethane, nitrile oxide and nitrone, have been investigated using DFT calculations at B3LYP/6-31G(d) level and the entire reaction surface has been explored. Two pathways are open for these reactions leading to two regiochemical products and in each way, the reaction can proceed in concerted or stepwise manner. In the stepwise process, there are two modes of attack, one leading to an allylic intermediate and the other an anti intermediate. A thorough search and analysis of these reaction paths show that stepwise modes are preferred over concerted modes, and regio 1 reaction prefers a stepwise path that involves a gauche intermediate whereas regio 2 reaction follows a stepwise path where an allylic intermediate is formed. Mainly the heteroatomic influence on the stability of diradical intermediates and other species in the reaction path and the cumulenic strain on allene determine the mechanism. Above factors also explain greater stability of allylic TS of regio 2 reaction compared to anti TS of regio 1 reaction, and this in turn explains the observed regioselectivity of the allene–diazomethane reaction. Computed deformation energies and bond orders establish that the favoured transition states are reactant-like and hence involve lower activation energies.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...