Modified purine nucleosides as dangling ends of DNA duplexes: the effect of the nucleobase polarizability on stacking interactions
Abstract
Base-modified nucleotide residues have been appended to the 5′-terminus of the self-complementary oligo-2′-deoxynucleotide duplex [5′-d(CGCGCG)]2 as dangling ends. Temperature-dependent UV measurements on the resulting oligomers indicate generally higher thermal stabilities (Tm) compared to that without an overhanging end. The duplex stabilization (ΔTm) was correlated with the molecular polarizability (αm) of the base of the pendant
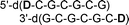

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...