Nanoporous iron oxide membranes: layer-by-layer deposition and electrochemical characterisation of processes within nanopores
Abstract
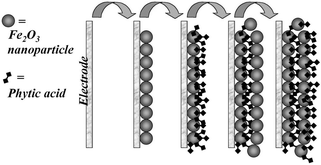
A versatile procedure for the formation of nanoporous metal
Mechanically stable and homogeneous nanofilm deposits with controlled thickness (ca. 3 nm per layer deposited) were obtained. Transport of small molecules or ions through the nanoporous structure and
their electrochemical conversion are shown to be fast in the presence of a sufficiently high concentration of supporting electrolyte. During the electrochemical oxidation of ferrocyanide, Fe(CN)64−, the nanoporous structure of the type A deposit is shown to act as an ‘active’ membrane, which changes the electrode kinetics by ‘double-layer superposition’ effects. For the second type of nanofilm, type B, ferrocyanide is accumulated by

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...