Facile synthesis of silver and bimetallic silver–gold nanoparticles and their applications in surface-enhanced Raman scattering†
Bharat Baruah* and
Meshack Kiambuthi
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Kennesaw State University, Kennesaw, GA 30144-5591, USA. E-mail: bbaruah@kennesaw.edu; Fax: + 1 470 578 9137; Tel: +1 470 578 2654
First published on 20th November 2014
Abstract
This study reports facile synthesis of monometallic and bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles using ascorbic acid as reducing agent. Monometallic silver nanoparticles (AgNP–CTAB–NA) with a bilayer of cationic surfactant, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) supported by n-nonylamine (NA) were first synthesized. Bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles, AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA, were synthesized using AgNP–CTAB–NA as precursor. We characterize AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy, UV-visible spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) line analysis. We demonstrate that both AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids are excellent surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates for Raman active analyte molecules at sub-micromolar concentrations.
1. Introduction
Bimetallic nanoparticles have received significant attention in recent years due to their outstanding optical,1 electrical2 and magnetic3 properties compared to monometallic nanoparticles. New surface properties4 evolve because of the combination of two metals. Technologically, bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles are superior to monometallic nanoparticles.5 Since properties of core–shell bimetallic nanoparticles depend on composition, shape, and size; control over the composition and morphology has been one of the main focuses of current research on bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles synthesis. To prepare bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles scientists have developed a variety of synthetic strategies, in both aqueous5,6 and non-aqueous7 solutions. Methods developed to synthesize bimetallic Au@Ag nanoparticles include borohydride reduction,8 citrate reduction,9 hydroxylamine reduction,6 microwave polyol method,10 photochemical reduction,11 sonochemical reduction,12 solvent-extraction reduction,13 etc. In addition, various surface protecting ligands have been utilized to generate stable bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles.5 Generation of bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles by reducing metal salts can be categorized into: co-reduction and successive reduction of two metal salts. Successive reduction is the commonly adopted method to prepare core–shell nanoparticles.14 Ag@Au core–shell nanoparticles have been extensively investigated in recent years. Yang and co-workers have recently reported the deposition of Au onto shrunken Ag templates to inhibit further oxidation of Ag, resulting in the formation of core–shell Ag–Au nanoparticles in toluene.15 Sun and co-workers demonstrated deposition of gold onto silver nanostructures to form Ag–Au alloys and then selective removal of silver from the alloyed wall in aqueous solution.16 Very recently, Selvakannan et al. used a transmetallation reaction between hydrophobized silver nanoparticle with hydrophobized chloroaurate and chloroplatinate ions in chloroform to generate hollow gold and platinum shell nanoparticles, respectively.17 Another study reports formation of both silver and gold nanoshells on polystyrene microspheres with diameters ranging from 188 to 543 nm, and by varying the amount of metal (silver and gold) reduced onto them, the surface plasmon resonance of the nanoshell could be tuned across the visible and the near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.18 Additionally, Gogoi et al. presented a novel method of generating free-standing and corrugated bimetallic NP Ag@Au thin films by using galvanic replacement reactions in the presence of CTAB.19 Development of facile alternative synthesis of Ag@Au nanoparticles of good water dispersibility would be of significant importance due their applications in sensors,20 DNA detection,21 colorimetric detection22 and SERS detection.14 The excellent SERS enhancement offered by Au@Ag14 is limited by an inherent tendency of silver to oxidize, which makes it less attractive than Ag@Au from the standpoint of stability and shelf-life.23Recently, there is an excitement about the potential use of SERS24 in concurrent multiplex detection of biological and chemical analytes. SERS is considered a simple, reliable, fast and inexpensive technique to provide the unique vibrational signature of analyte in aqueous solution. SERS is an extension of regular Raman spectroscopy and the enhancement effect arises due to electronic and chemical interactions between the excitation laser, analyte and the SERS substrate.14,25 Modification of metal surfaces and generation of core–shell alloy nanoparticles significantly alter the SERS effect. Qian et al. have synthesized Ag@Au in presence of CTAB.26 However, these nanoparticles do not have uniform size distribution and the precursor AgNP are synthesized by traditional citrate method and no applications has been demonstrated. Very recently, He et al. reported a work on AgNP@Au where a negatively charged surface was modified to a positively charged surface in order for the electrostatic attachment of a negatively charged enzyme for optical glucose sensing.27 Mirkin group28 and the Li group29 have demonstrated that nanoparticles with positively charged surface is essential in order to bind negatively charged biomolecules like DNA. Such applications clearly justify development of facile synthesis of monometallic and bimetallic nanoparticles with positively charged surfaces as opposed to traditional negatively charged citrate-capped nanoparticles.
In the current study, we prepare monometallic, AgNP–CTAB–NA and bimetallic core–shell, AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids where particles are coated with a bilayer of CTAB supported by NA. Such colloidal suspensions where metal nanoparticles are coated with surfactant are called admicelle.30 It is known that a bilayer of CTAB stabilizes metal structures in aqueous solutions.31–33 In the current admicelles, AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA, NA appears to reside between CTAB bilayers as a co-surfactant. Nanoparticles were previously stabilized with interdigitated CTAB by electrochemical31,32 and phase transfer methods.34 It is widely accepted that CTAB interdigitated bilayer on nano-surfaces.31–33,35–37 In particular, it has been shown that the intercalation of aromatic compounds such as sodium salicylate between the CTAB headgroups results from the synergistic electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions.37 Inspired by the knowledge on the behavior of aromatic compounds in the nano-surface bound bilayer of CTAB, we exploit the possibility of CTAB bound monometallic and bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles as SERS substrate for aromatic analytes. We tested the SERS activity of AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA utilizing a Raman active dye, crystal violet (CV). AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA were characterized by 1H NMR, UV-Visible, FTIR, DLS, HR-TEM, and EDX line analysis and tested for SERS activity using Raman spectroscopy.
2. Results and discussion
Recent reports document that CTAB has been utilized to stabilize monometallic38 and bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles.26 In most cases CTAB form a bilayer on metal nanoparticles32,33 and is known to better stabilizes nanorods compared to nanospheres.32 The CTAB bilayer provides the nanorods charge, stability and water solubility in addition to a ∼3–4 nm thick hydrophobic region on the gold surface due to the interdigitated 16-carbon chain of CTAB.32,33 We have found that spherical monometallic AgNP and bimetallic core–shell AgNP@Au could be stabilized in aqueous solutions with an adsorbed CTAB bilayer in presence of partially water soluble alkylamine, such as n-nonylamine (NA). In these systems NA serves as a cosurfactant.In this study we report synthesis of monometallic AgNP–CTAB–NA and bimetallic AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids. Molecular structures of CTAB and NA are shown in Fig. 1. In a typical synthetic procedure, AgNP–CTAB–NA colloids were prepared by reducing silver nitrate, AgNO3 with ascorbic acid in an aqueous solution of CTAB and NA. After 24 h yellow AgNP–CTAB–NA colloids were centrifuged, supernatant was discarded and finally particles were dispersed in DI water and stored for further use. Similarly, AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids were prepared by reducing NaAuCl4 with ascorbic acid in an aqueous solution of CTAB and NA in presence of AgNP–CTAB–NA seeds. After 24 h red AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids were centrifuged, supernatant was discarded and finally particles were dispersed in DI water and stored for further use. In both the colloids CTAB bilayer remains adsorbed on the metal surface and forms admicelle.30 The 16-carbon tails of the CTAB interdigitates and forms the hydrophobic shell and NA resides in that shell.36 The presence of NA between interdigitated CTAB molecules provides tighter curvature39 and thereby renders better stability. CTAB further provide an overall positive charge to the monometallic and bimetallic colloids.36 Both AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids serve as excellent SERS substrate. Scheme 1 presents the complete synthetic protocol.
2.1 Characterization of colloids by UV-visible spectroscopy
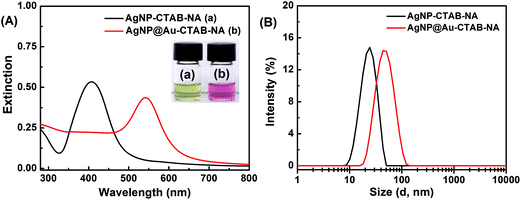
Fig. 2A(a) shows the UV-visible spectrum of silver nanoparticles, AgNP–CTAB–NA synthesized with CTAB and NA as capping agents. AgNP–CTAB–NA exhibits a well-defined SPR band with a maximum absorbance at 407.2 ± 1.4 nm with a FWHM (full width at half maximum) of 81 nm, which is similar to that of previously reported silver nanoparticles.40 Spectrum (b) shows bimetallic core–shell AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids with a SPR band centered at 542.3 ± 2.0 nm with a FWHM of 72 nm. The inset of Fig. 2A also shows corresponding digital photographs of the samples used for the UV-visible spectroscopy as discussed above.2.2 Size and zeta potential of nanoparticles with dynamic light scattering
We measured particle size distribution (PSD) of AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA with dynamic light scattering (DLS) as shown in Fig. 2B. AgNP–CTAB–NA exhibits a mean hydrodynamic diameter of 25.6 ± 0.2 nm (average PDI = 0.276). AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids synthesized from the AgNP–CTAB–NA are monodispersed with a mean hydrodynamic diameter of 46.9 ± 0.6 nm (average PDI = 0.228) (Fig. 2B).Table 1 reports zeta potential values obtained from the electrophoretic mobility measurements for the colloid samples. The surface charge41 of the nanoparticles and the pH of the solutions41 directly relate to their stability. We measured zeta potential of both the colloid samples at pH 7.3 to verify their stability. Zeta potentials for AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids are +36.0 ± 2.0 and +35.0 ± 2.0, respectively. The positive zeta potential value of both the colloids indicate presence of CTAB layer at the metal nanoparticle surface.
| Colloidal samples | Zeta potential (mV) |
|---|---|
| AgNP–CTAB–NA | +36.0 ± 2.0 |
| AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA | +35.0 ± 2.0 |
2.3 TEM images and EDX analysis of colloids
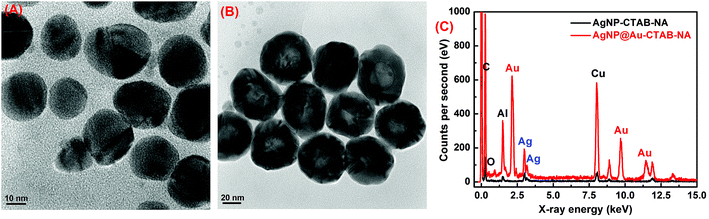
The images of the nanoparticles were visualized using HR-TEM. The HR-TEM images of monometallic AgNP–CTAB–NA and bimetallic core–shell AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids are shown in Fig. 3A and B, respectively. From the HR-TEM images it can be seen that AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA particle sizes are consistent with the results obtained by DLS measurements in solution.EDX measurement was carried out to determine the elemental composition of the synthesized monometallic and bimetallic nanoparticles. The absorption peak of Ag is around 3 keV for both AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA (Fig. 3C), which is in accordance with the previously reported value, and this has been attributed to SPR.42 AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA nanoparticles showed strong signals for Au (Fig. 3C). Another relatively strong background signal was seen at ∼8 keV. This signal is due to Cu as copper grids were used in the analysis. Since EDX is a semi-quantitative technique,43 one could use it to determine the Ag![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Au ratio within the nanoparticles. The proportions of Ag and Au, which were measured using EDX, are 12.41 weight% and 50.58 weight%, respectively for AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA.
Au ratio within the nanoparticles. The proportions of Ag and Au, which were measured using EDX, are 12.41 weight% and 50.58 weight%, respectively for AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA.
2.4 Characterization of AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloid by 1H NMR spectroscopy
Fig. 4 shows the 1H NMR spectra recorded for CTAB, NA, physical mixture of NA and CTAB, AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloid in D2O. We identified all the signals in the spectra as follows. The signals for CTAB (spectrum a) appear at 3.40 (C1′), 3.18 (N(CH3)3), 1.79 (C2′), 1.31 (C3′–C15′), and 0.89 (C16′) ppm. 1H NMR signals for NA (spectrum b) appear at 2.97 (C1), 1.64 (C2), 1.28 (C3–C8), and 0.85 (C9) ppm. These assignments correspond to the labels used in Fig. 1. Signals for NA in the NA and CTAB physical mixture (spectrum c) appear at 2.97 (C1), 1.64 (C2), 1.30 (C3–C8), and 0.86 (C9) ppm. For AgNP–CTAB–NA conjugates (spectrum d) the signals for NA appear at 2.92 (C1), 1.61 (C2), 1.28 (C3–C8), and 0.85 (C9) ppm. A comparison of the 1H NMR spectrum for NA (spectrum b) with that of AgNP–CTAB–NA (spectrum d) show 0.05 ppm upfield shift for C1 and 0.03 ppm upfield shift for C2 protons in AgNP–CTAB–NA. This indicates that amine group of NA molecules bind the silver surface (Scheme 1) and cause upfield shift to the protons attached to the adjacent carbon atoms (C1 and C2). For AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids (spectrum e) the signals for NA appear at 2.97 (C1), 1.64 (C2), 1.24 (C3–C8), and 0.82 (C9) ppm. A comparison of the 1H NMR spectrum for NA (spectrum b) with that of AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA (spectrum d) shows a 0.04 ppm upfield shift for C3–C8 and 0.03 ppm upfield shift for C9 protons in AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA.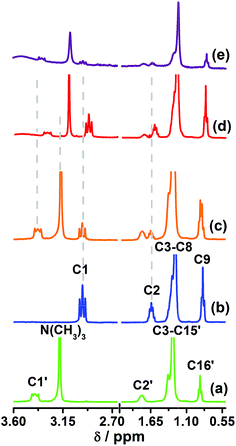 | ||
| Fig. 4 1H NMR spectra of (a) CTAB, (b) NA, (c) physical mixture of NA and CTAB, (d) AgNP–CTAB–NA and (e) AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA. All the signals assigned according to the proton labels shown in Fig. 1. | ||
The signals for CTAB in the NA and CTAB physical mixture (spectrum c) appear at 3.40 (C1′), 3.18 (N(CH3)3), 1.78 (C2′), 1.30 (C3′–C15′), and 0.89 (C16′) ppm. The signals in spectrum (a) show no significant differences with the CTAB signals in NA and CTAB physical mixture (spectrum c). The CTAB signals in AgNP–CTAB–NA (spectrum d) appear at 3.30 (C1′), 3.10 (N(CH3)3), 1.74 (C2′), 1.24 (C3′–C15′), and 0.80 (C16′) ppm. In AgNP–CTAB–NA conjugates (spectrum d) signals for C1′ and (N(CH3)3) exhibit upfield shift of 0.10 and 0.08 ppm, respectively compared to CTAB only sample (spectrum a). This shift is due to the presence of CTAB molecules bound to the metal surface with –N(CH3)3 facing the surface. However, there should be CTAB molecules with –N(CH3)3 facing the bulk water to provide overall positive charge to the nanoparticles. The 1H NMR chemical shift for CTAB in AgNP–CTAB–NA conjugates is essentially an average shift of interdigitated CTAB molecules,35–37 possibly half of them facing the bulk water and the other half facing the metal surface as illustrated in Scheme 1. The CTAB signals in AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA (spectrum e) appear at 3.35 (C1′), 3.10 (N(CH3)3), 1.76 (C2′), 1.24 (C3′–C15′), and 0.80 (C16′) ppm. A comparison of the 1H NMR spectrum for CTAB (spectrum a) with that of AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA (spectrum e) exhibit upfield shifts of 0.05, 0.08, 0.02, 0.06 and 0.09 ppm, respectively for C1′, N(CH3)3, C2′, C3′–C15′, and C16′ protons in the later. Among these, the signal for –N(CH3)3 shifts second most. This suggests that the CTAB molecules bind to the surface of the bimetallic AgNP@Au through the quaternary ammonium headgroup. However, there should be CTAB molecules with –N(CH3)3 facing the bulk water to provide overall positive charge to the nanoparticles. The 1H NMR chemical shift for CTAB is essentially an average shift of interdigitated CTAB molecules as reported previously.35–37
2.5 Characterization of colloids by FTIR spectroscopy
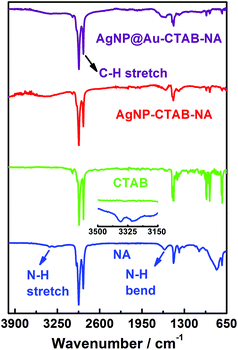
FTIR spectroscopic data suggests the presence of CTAB and NA bound to the surface of metal in the colloidal sample. We plot the FTIR spectra of NA, CTAB, AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA in Fig. 5. NA gives peaks at 3388/3348, 2934/2857, 1615 and 1464 cm−1 that are assigned to N–H stretch, C–H stretch, N–H bending and C–H bending. CTAB gives peaks at 2921/2876 and 1477 cm−1 that are assigned to C–H stretch and C–H bending. For AgNP–CTAB–NA colloid a broad peak appear at 3422 attributed to N–H stretch; 2928/2851 for C–H stretch, 1596 for N–H bending and 1468 cm−1 C–H bending. For AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloid a broad peak appear at 3371 attributed to N–H stretch; 2934/2857 for C–H stretch, 1594 for N–H bending and 1477 cm−1 for C–H bending. For both AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids presence of characteristic N–H and C–H signals clearly indicate that the nanoparticles surface have been capped with CTAB and NA layer.2.6 Monometallic and core–shell bimetallic colloids as SERS substrate
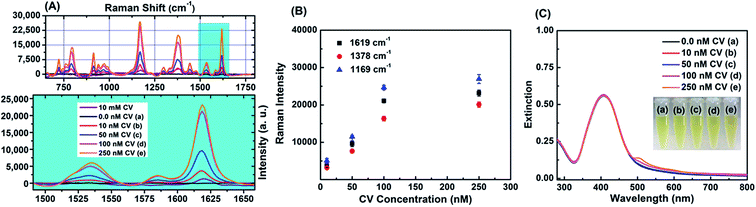
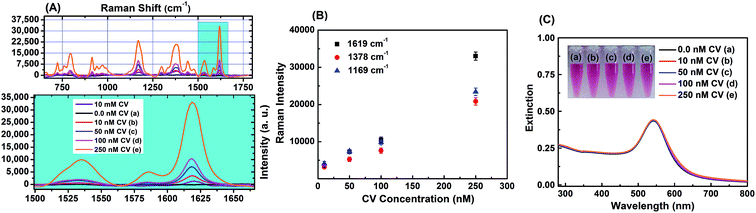
Surface modified gold nanostructures can sustain44 the SPR band in the presence of a variety of organic analyte molecules, and this makes them suitable for SERS application. Pande et al. reported14 the influence of the shell material in a β-CD capped bimetallic core–shell nanoparticle on the SERS signal enhancement in solution using 1,10-phenanthroline as a molecular probe. Another report6 demonstrated large SERS enhancement for biomolecules by citrate capped bimetallic Ag@Au nanoparticles compared to monometallic silver nanoparticles. The monometallic AgNP–CTAB–NA and bimetallic core–shell AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA nanoparticles, discussed here were tested as SERS substrates and SERS activity has been successfully demonstrated with the common analyte molecule, CV.We systematically studied the effect of concentration variation of the Raman dye CV to demonstrate the detection limit of CV in presence of AgNP–CTAB–NA colloids. Fig. 6A shows the Raman spectra of 10 mM CV in MeOH (purple line), AgNP–CTAB–NA without CV (black line) and SERS spectra of various concentrations of CV with AgNP–CTAB–NA. The concentration of CV was varied from 10.0 nM to 250 nM. The SERS signal of CV with AgNP–CTAB–NA is noticeably enhanced in all four samples containing 10 nM (red line), 50 nM (blue line), 100 nM (pink line) and 250 nM (orange line) CV. In all these samples, an aliquot of CV from 2.5 μM or 50 μM CV in methanol was added to a 1.0 mL aqueous solution of AgNP–CTAB–NA and then incubated for 1 h before Raman spectroscopic measurements. Fig. 6A shows the surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra for CV with concentrations ranging between 0 and 250 nM, at an excitation wavelength of 633 nm. Whereas very strong SERS signals were detected from 50 nM to 250 nM, the intensities at 10 nM are relatively low, but all the main modes at 1619, 1378, 1169, 913, 796, and 722 cm−1 can be clearly identified. The Raman vibrations are assigned according to previous literature report45 as strong ring C–C stretching at 1619 cm−1, N-phenyl stretching at 1378 cm−1, ring C–H bending at 1169 cm−1, medium δ(CCcenterC) at 913 cm−1, medium signal at 796 cm−1, and weak ν(CN) at 722 cm−1.
SERS performance was quantified by determining the enhancement factor. In colloidal solutions, the analytical enhancement factor (AEF) of a nanoparticle conjugate can be estimated from the ratio of SERS intensity for the selected mode of a given analyte (ISERS) and the corresponding Raman intensity (IRS) under identical experimental conditions (e.g. sample preparation, laser wavelength and power, integration time etc.) using the following equation:46
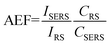 | (1) |
In eqn (1) CSERS and CRS are the concentrations of the analyte in the SERS and Raman experiments, respectively. With CRS = 0.01 M, CSERS = 2.5 × 10−7 M, IRS (1620 cm−1) = 1489, and ISERS (1619 cm−1) = 23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 188, the AEF was estimated to be 6.2 × 105. This value lies within the highest AEF presented in the literature for metal nanoparticle colloids.46 Fig. 6B represents the plot of Raman intensity versus concentration of CV for the most intense Raman active signals namely 1169, 1378, and 1619 cm−1. With the increase in concentrations the Raman intensity increases. Raman mode at 1169 cm−1 has the highest intensity and at 1378 cm−1 has the lowest intensity. This trend is consistent for all the four concentrations of CV used in this work.
188, the AEF was estimated to be 6.2 × 105. This value lies within the highest AEF presented in the literature for metal nanoparticle colloids.46 Fig. 6B represents the plot of Raman intensity versus concentration of CV for the most intense Raman active signals namely 1169, 1378, and 1619 cm−1. With the increase in concentrations the Raman intensity increases. Raman mode at 1169 cm−1 has the highest intensity and at 1378 cm−1 has the lowest intensity. This trend is consistent for all the four concentrations of CV used in this work.
Fig. 6C represents the corresponding SPR bands of the above colloid samples of AgNP–CTAB–NA without and with CV. In sample (e) (the orange line) there is an additional peak at ∼510 nm attributed to the absorbance from 250 nM CV. The inset in Fig. 6C shows the digital pictures of these samples in presence of various concentrations of CV.
The SERS signal of CV with AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA systematically increase similar to that with AgNP–CTAB–NA as shown in Fig. 7A. SERS performance for AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA was quantified by determining the enhancement factor using eqn (1) with CRS = 0.01 M, CSERS = 2.5 × 10−7 M, IRS (1620 cm−1) = 1489, and ISERS (1619 cm−1) = 33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 014, the AEF was estimated to be 8.9 × 105. This value lies within the highest AEF presented in the literature for metal nanoparticle colloids.47 Fig. 7B represents the plot of Raman intensity versus concentration of CV. Raman mode at 1619 cm−1 has the highest intensity and at 1378 cm−1 has the lowest intensity. This trend is consistent for 100 nM and 250 nM CV. However, for 5 nM and 10 nM CV, the intensities of Raman mode at 1619 and 1169 cm−1 overlap. For Raman mode at 1378 cm−1 the intensity is lowest at both 5 nM and 10 nM CV.
014, the AEF was estimated to be 8.9 × 105. This value lies within the highest AEF presented in the literature for metal nanoparticle colloids.47 Fig. 7B represents the plot of Raman intensity versus concentration of CV. Raman mode at 1619 cm−1 has the highest intensity and at 1378 cm−1 has the lowest intensity. This trend is consistent for 100 nM and 250 nM CV. However, for 5 nM and 10 nM CV, the intensities of Raman mode at 1619 and 1169 cm−1 overlap. For Raman mode at 1378 cm−1 the intensity is lowest at both 5 nM and 10 nM CV.
In Fig. 7C the corresponding UV-visible spectra of AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloidal solutions are shown along with their digital pictures in the inset. There is no variation in the color in the digital picture or in the UV-visible absorption position. This indicates that these samples are stable in the presence of CV. All the samples were prepared as described below in methods section.
The data on SERS enhancement for most intense Raman shift 1169, 1378, and 1619 cm−1 are summarized in Table 2. The most intense Raman shifts of CV are at 1173, 1380, 1620 cm−1 for pure CV, while they shift to 1169, 1378, and 1619 cm−1 upon interacting with the colloidal surface. This downshift likely arises from the hydrophobic incorporation of CV into the bilayer. For both colloidal systems AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA the surfactant bilayer has a positive charge and the Raman probe CV has a positive change. Electrostatically, they should repel each other and as result there should not be any enhancement to the active Raman modes of CV. However, due to hydrophobic interactions the hydrophobic CV molecules embeds in the CTAB and NA layer and thereby come closer to metal surface. As indicted in Table 2 for AgNP–CTAB–NA colloids, the Raman mode at 1619 cm−1 has the highest AEF of 6.2 × 105 and Raman mode at 1378 cm−1 has minimum AEF of 3.3 × 105. Similarly, for AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids the Raman mode at 1378 cm−1 has the lowest AEF of 3.0 × 105 and Raman mode at 1619 cm−1 has maximum AEF of 8.9 × 105. For both colloidal systems AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA the enhancement factors are comparable and are in the order of 105. This phenomenon further indicates that for both colloid types, monometallic and bimetallic core–shell, in this case, have same surface properties and this ensures very similar interactions of bilayer covered nanoparticles and hydrophobic Raman probe such as CV.
| Sample | Raman shift (cm−1) | SERS intensity | CV (nM) | AEF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNP–CTAB–NA | 1169 | 26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 939 ± 1200 939 ± 1200 |
250 | (5.2 ± 0.3) × 105 |
| AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA | 1169 | 23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 415 ± 1000 415 ± 1000 |
250 | (4.1 ± 0.6) × 105 |
| AgNP–CTAB–NA | 1378 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 097 ± 700 097 ± 700 |
250 | (3.3 ± 0.4) × 105 |
| AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA | 1378 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 841 ± 1000 841 ± 1000 |
250 | (3.0 ± 0.5) × 105 |
| AgNP–CTAB–NA | 1619 | 23![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 188 ± 800 188 ± 800 |
250 | (6.2 ± 0.2) × 105 |
| AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA | 1619 | 33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 014 ± 1100 014 ± 1100 |
250 | (8.9 ± 0.2) × 105 |
A recent report showed6 that SERS enhancement can be tuned, maximized and geared towards biological applications for core–shell nanoparticles by managing the hot spots. In a similar study Schwartzberg et al. reported48 that dye molecules may readily bind gold nanoparticles, and thereby aggregate them and exhibit strong SERS activity. In our current systems, AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA, hydrophobic CV molecule most probably penetrates the hydrophobic area of CTAB–NA bilayer, and then possibly resides in the bilayer resulting from the hydrophobic interactions37 and thus exists within the electromagnetic (EM) field generated by the metal surface during the Raman measurement and thereby generating strong SERS signals.
2.7 Location of CV in the colloidal solutions and possible SERS mechanism
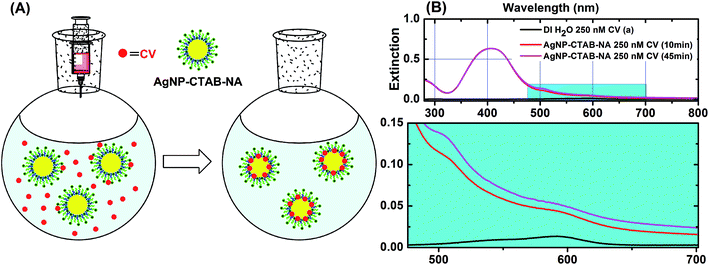
In order to demonstrate the location of CV we have performed another set of experiment. When CV is added to the colloidal solutions, it slowly get incorporated to the CTAB bilayer (Fig. S4†) or adsorbed on metal surface as depicted in Fig. 8 panel (A). UV-visible spectrum of AgNP–CTAB–NA with 250 nm CV after 10 minutes of addition shows (Fig. 8B, red line) a drastic change with appearance of an absorption maxima at ∼510 and a shoulder at ∼590. In the spectrum of CV in DI water (Fig. 8B, black line) the absorption maxima is at ∼590 nm and shoulder is at ∼520 nm. After 45 minutes (Fig. 8B, pink line) the intensity of the maxima at ∼510 increases further. This change in shape of UV-visible spectrum is attributed to metachromasy of CV.49 Crystal violet is positively charged organic dye. It is mostly hydrophobic, however, due to presence of positive charge it is also water soluble to some extent.49 A typical absorption spectrum of CV has a maxima at ∼590 nm and a shoulder at ∼550 nm below 10−4 M concentration.49 In more concentrated solution (∼10−3 M) the absorption maximum is ∼550 nm and the shoulder is ∼590 nm.49 This change in shape of absorption maximum is called metachromasy and is due to aggregation of dye molecules in to dimers, trimmers, and higher order aggregates.49 The observed changes in AgNP–CTAB–NA absorption spectra containing 250 nM CV is clear indication of metachromasy of CV. In presence of AgNP–CTAB–NA the CV molecules are adsorbed so close on to the ∼26 nm metal surface that they behave as aggregates spectrally49 as shown in Fig. 8A. In case of AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA, the particle size is ∼47 nm and CV molecules only incorporated in the CTAB–NA bilayer due to hydrophobic interactions but not directly adsorbed on to the surface of Au and potentially do not show aggregation and thereby no metachromasy is observed (Fig. S4†).SERS enhancement could be due to primarily two mechanisms, electromagnetic enhancement (EM) and chemical enhancement via charge transfer (CT).25,50 Both are interrelated and cannot be separated easliy.25,50 EM enhancement is observed when the incoming laser excites the surface plasmons of metal and creates an electromagnetic field which could extended up to 20 nm from the metal surface.25 This could enhance the Raman signal of exposed analyte by an order of 104 time.25 CT between analyte and the metal surface due to direct contact of analyte and metal could contribute an additional 10–100 times enhancement. Further enhancement is possible if the applied laser wavelength falls near an absorption wavelength of the sample. This is known as resonance enhancement.25 The excitation wavelength of used laser line in this study is 633 nm and the SPR band of AgNP–CTAB–NA (407 nm) do not overlap closely with this. However, the SERS enhancement is in the order of 105 for this system (Table 2). For AgNP–CTAB–NA the contributions should be from EM and CT.25,50,51 As described above the CV molecules are adsorbed on to the silver surface due to hydrophobic incorporation by the CTAB bilayer (Fig. 8A) and this allows CT between silver and the CV molecules. In contrast, the SPR band of AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA is at 542 nm and is relatively closer to the utilized laser line at 633 nm. The absorption maximum of 250 nM CV in presence AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA is not visible as shown in Fig. 7C. However, a subtraction spectrum between AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA with 250 nM CV and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA with 0.0 nM CV gives spectrum of CV only. This spectrum is shown in panel B (blue line) of Fig. S4 (ESI†). This clearly indicates that there is no metachromasy of CV molecule in this case and CV molecules are not directly adsorbed on to the metal surface.49 However, the hydrophobic incorporation of CV by CTAB bilayer brings them closer to the metal surface and are within the generated EM field (Fig. S4A, ESI†). Hence, the SERS enhancements are due to EM and to some extent resonance contribution.25,50 A subtraction spectrum of between AgNP–CTAB–NA with 250 nM CV and AgNP–CTAB–NA with 0.0 nM CV gives spectrum of CV only as shown in panel B (red line) of Fig. S4 (ESI†). This is a definite case of metachromasy49 of CV molecule due to selective adsorption of on Ag surface as described earlier. This selective adsorption of CV to Ag surface is due to greater affinity of N-atom in CV towards silver based on Hard-Soft Acid-Base principle.52 That is why in AgNP–CTAB–NA the SERS enhancement is due to EM and CT.25,50 Alternatively, the N-atom of CV has weaker affinity towards Au surface52 and do not directly get adsorbed to the Au surface in AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA. In this case CV molecules get closer to the Au surface due to hydrophobic incorporation of CV by CTAB bilayer and EM and resonance enhancement25,50 are dominant in the SERS spectra as demonstrated previously.36 The produced electromagnetic field due to interactions of incident laser and surface plasmons could be extended up to 20 nm.25 As AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA is ∼47 nm in size as opposed to ∼26 nm of AgNP–CTAB–NA, the former would produce an extended EM field. The combination of “extended EM and resonance” in AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA and combination of “EM and CT” in AgNP–CTAB–NA produces comparable SERS enhancement in the order of 105 (Table 2).
3. Experimental
3.1 Materials
NaAuCl4·2H2O (99%), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (≥99%), and crystal violet (CV) (99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; AgNO3 (99%), ascorbic acid (98%), and n-nonylamine (98.0%) were purchased from Across Organic; cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (97.5%) was purchased from Fisher Scientific. All chemicals and solvents were used without further purification. All glassware were cleaned with aqua regia (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v HCl (37%)–HNO3 (65%) solutions) and then rinsed thoroughly with DI H2O before use. Caution: aqua regia solutions are dangerous and highly corrosive. This should be used with extreme care. Fresh aqua regia solutions should not be stored in closed containers. The DI water in all experiments was Milli-Q water (18 MΩ cm, Millipore).
1 v/v HCl (37%)–HNO3 (65%) solutions) and then rinsed thoroughly with DI H2O before use. Caution: aqua regia solutions are dangerous and highly corrosive. This should be used with extreme care. Fresh aqua regia solutions should not be stored in closed containers. The DI water in all experiments was Milli-Q water (18 MΩ cm, Millipore).
3.2 Synthesis of CTAB–NA capped monometallic silver colloids (AgNP–CTAB–NA)
To 8.9 mL of DI water added 1.0 mL of 5.0 mM CTAB and 5.0 mM NA mixture with subsequent addition of 50 μL of 100 mM AgNO3. This mixture was stirred for 5 minutes and then 50 μL of 100 mM ascorbic acid was added and further stirred for additional 15 minutes. The solution color slowly turned from colorless to light yellow to dark yellow. Thus formed AgNP–CTAB–NA was purified by centrifuging at 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm for 15 minutes in 1.5 mL batches in 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes. The supernatant was discarded and the sample was redispersed in 1.5 mL pure DI water. The centrifugation as above was repeated twice and colloids were stored for further application.
000 rpm for 15 minutes in 1.5 mL batches in 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes. The supernatant was discarded and the sample was redispersed in 1.5 mL pure DI water. The centrifugation as above was repeated twice and colloids were stored for further application.
3.3 Synthesis of CTAB–NA capped bimetallic core–shell colloids (AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA)
50 mL of 0.233 mM NaAuCl4 was diluted with 50 mL of DI water and 10 mL of 5.0 mM CTAB and 5.0 mM NA mixture. The solution was further stirred for 5 minutes when the solution color changed from light yellow to bright yellow. Then 10 mL of AgNP–CTAB–NA was added dropwise, the solution color slowly turned brownish. After this 500 μL of 100 mM ascorbic acid was added to this mixture with constant stirring. The solution was further stirred for another 30 minutes when the solution colored turned reddish purple indicating formation of AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA. AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA thus formed was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 15 minutes in 1.5 mL batches in 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes. After that the supernatant was discarded and the sample was redispersed in 1.5 mL pure DI water. The centrifugation as above was repeated twice and colloids were stored for further application.3.4 1H NMR spectroscopic characterization of nanoparticles
1H NMR data were collected using a Bruker DPX 300 MHz NMR spectrometer with a resonance frequency of 300.13 MHz. 1H chemical shifts were referenced against 4,4-dimethyl-4-silapentanesulfonate, sodium salt (DSS) with a coaxial inner tube containing 50 μL of 5.0 mM DSS in D2O. 1H NMR spectra were acquired with 64 transients, 3.16 kHz spectral window, a 60° pulse angle, and a 10.4 s acquisition time with relaxation delay of 1.0 s. For peak position measurements, a 0.3 Hz exponential line broadening was applied before Fourier transformation for all data. All NMR data were processed using MestReNova v5.30 for Windows and plotted using Origin 8.0.3.5 UV-visible and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic studies of nanoparticles
The absorption spectrum was recorded using a Cary 4000 UV-visible spectrophotometer. FTIR spectroscopy was performed using Perkin-Elmer FTIR Spectra 100 spectrometer fitted with diamond ATR.3.6 Raman spectroscopic measurement
The CV containing AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids are well monodispersed in pure DI water. 2.5 μM and 50 μM solutions of CV in methanol are used as stock. Typical samples for SERS contained 1.0 mL of AgNP–CTAB–NA or AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids dispersed in pure DI water and added an aliquot of 4.0 or 20 μL of 2.5 μM CV (in MeOH) so that the final concentration of CV are 10 or 50 nM; added an aliquot 2.0 or 5.0 μL of 50 μM CV (in MeOH) so that the final concentration of CV are 100 and 250 nM. Samples are allowed to stand for 1 hour before Raman spectroscopic measurements are carried out on a DeltaNu Advantage 200A Raman spectrometer. This instrument is equipped with a HeNe laser set at 632.8 nm for all measurements. Integration time for all measurements was 5.0 s. The Raman spectrum of 10 mM CV was acquired with an integration time of 1.0 s. However, the spectral resolution of 10 mM CV was poor as its Raman signal sits on top of a strong fluorescence background.533.7 Electron microscopy and EDX analysis
High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) images were collected with a H9500 with LaB6 source of resolution =0.1 nm at 300 kV. Nanoparticle samples prepared in DI water and were centrifuged and redispersed in DI water. These solutions were filtered with 200 nm syringe filters before applying on grids for TEM measurements. Samples were prepared by spreading a 3.0 μL of colloidal sample on an ultrathin 300 mesh Formvar/carbon-coated copper grid, dried in air. Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) line analysis was performed using Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM) HD2000 with Field Emission source of resolution 0.24 nm at 200 kV.3.8 Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements
The mean hydrodynamic diameter of AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids were determined using dynamic light scattering with a commercial Zetasizer (Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments). Samples were loaded into disposable cells and measured the particle sizes twice and in triplicate. Zeta potential was measured by loading samples in regular disposable cells and using a dip probe.4. Conclusions
In summary, facile synthesis of AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids have been reported. AgNP–CTAB–NA colloids were synthesized by reducing AgNO3 by ascorbic acid at room temperature in presence of CTAB and NA in aqueous solutions. Similarly, AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids were achieved simply by adding a layer of gold on AgNP–CTAB–NA colloids. The bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles, AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA, reported here are ∼21 nm larger than its precursor, AgNP–CTAB–NA. DLS and HR-TEM data support this size increase. FTIR and 1H NMR data support the presence of CTAB and NA on the gold surface on both AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA. UV-visible spectroscopic data supports the HR-TEM size data and exhibit red shift of the SPR band from AgNP–CTAB–NA to AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids. EDX line analysis support the presence of Ag in AgNP–CTAB–NA colloids and both Ag and Au in AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids.In this report, we have shown that both monometallic AgNP–CTAB–NA and bimetallic core–shell AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA colloids significantly enhance the SERS intensities of adsorbed analyte molecules with AEF in the order of 105. Such SERS enhancement phenomenon is thought to be driven by combined EM and CT mechanism in AgNP–CTAB–NA due to direct adsorption of CV on silver surface due to greater affinity of Ag towards N-atom bearing CV molecules.52 In case of larger AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA the analyte gets incorporated in the hydrophobic bilayer of CTAB and NA and as such exists within the relatively larger electromagnetic (EM) field generated by the metal surface during the Raman measurement and the laser wavelength is also closer to the SPR band of this colloid. Thereby AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA generates strong SERS signal due to EM and resonance enhancments.25,36 CV molecules do not get directly adsorbed on the gold surface due to weaker affinity of Au towards N-atom bearing CV molecules.52 Thus, overall adsorption of analytes on hydrophobic bilayer of admicelles AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA could have potential implications in the field of nanomedicine54–56 and selective SERS detection6,14 of certain chemical and biological analytes. The proposed colloids, AgNP–CTAB–NA and AgNP@Au–CTAB–NA set the stage for further development of bilayer capped nanoparticle-based rapid, sensitive and inexpensive detection of analytes by simple SERS methods. Both colloids give a SERS signal at as low as 5.0 nM of CV. Further studies are currently in progress.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Kennesaw State University, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, KSU CSM Mentor Protégé fund (BARUAH20FY2013-01) awarded to Bharat Baruah. BB would like to thank Dr Mark Mitchell, Department Chair; Dr Mark Anderson, Dean of the College of Science and Mathematics for their enormous support. We acknowledge Advanced Materials Research Laboratories (AMRL) at Clemson University for HRTEM and EDX analysis. B.B. is thankful to Dr David Gottfried at Georgia Institute of Technology, IEN for the support with dynamic light scattering experiments.Notes and references
- A. Henglein and C. Brancewicz, Chem. Mater., 1997, 9, 2164–2167 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. J. Hostetler, C.-J. Zhong, B. K. H. Yen, J. Anderegg, S. M. Gross, N. D. Evans, M. Porter and R. W. Murray, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 9396–9397 CrossRef CAS
.
- N. Toshima, T. Yonezawa, M. Harada, K. Asakura and Y. Iwasawa, Chem. Lett., 1990, 19, 815–818 CrossRef
.
- J. H. Sinfelt, Bimetallic Catalyst:
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Discoveries Concepts and Application, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1983 Search PubMed
Discoveries Concepts and Application, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1983 Search PubMed .
- R. Ghosh Chaudhuri and S. Paria, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 2373–2433 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. V. P. Kumar, S. Shruthi, B. Vibha, B. A. A. Reddy, T. K. Kundu and C. Narayana, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 4388–4392 CAS
.
- S. Nath, S. Praharaj, S. Panigrahi, S. K. Ghosh, S. Kundu, S. Basu and T. Pal, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 10405–10408 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- H. M. Chen, R. S. Liu, L. Y. Jang, J. F. Lee and S. F. Hu, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2006, 421, 118–123 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Link, Z. L. Wang and M. A. El-Sayed, J. Phys. Chem. B, 1999, 103, 3529–3533 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Tsuji, M. Nishio, P. Jiang, N. Miyamae, S. Lim, K. Matsumoto, D. Ueyama and X.-L. Tang, Colloids Surf., A, 2008, 317, 247–255 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C. M. Gonzalez, Y. Liu and J. C. Scaiano, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 11861–11867 CAS
.
- S. Anandan, F. Grieser and M. Ashokkumar, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 15102–15105 CAS
.
- O. M. Wilson, R. W. J. Scott, J. C. Garcia-Martinez and R. M. Crooks, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 127, 1015–1024 CrossRef PubMed
.
- S. Pande, S. K. Ghosh, S. Praharaj, S. Panigrahi, S. Basu, S. Jana, A. Pal, T. Tsukuda and T. Pal, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 10806–10813 CAS
.
- J. Yang, J. Y. Lee and H.-P. Too, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 19208–19212 CrossRef PubMed
.
- Y. Sun and Y. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 3892–3901 CrossRef PubMed
.
- P. R. Selvakannan and M. Sastry, Chem. Commun., 2005, 1684–1686 RSC
.
- K.-T. Yong, Y. Sahoo, M. T. Swihart and P. N. Prasad, Colloids Surf., A, 2006, 290, 89–105 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. K. Gogoi, A. Paul and A. Chattopadhyay, RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 3642–3646 RSC
.
- D. Tang, R. Yuan and Y. Chai, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2006, 94, 996–1004 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. C. Cao, R. Jin, C. S. Thaxton and C. A. Mirkin, Talanta, 2005, 67, 449–455 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- T. Lou, L. Chen, Z. Chen, Y. Wang, L. Chen and J. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2011, 3, 4215–4220 CAS
.
- F. L. Yap, P. Thoniyot, S. Krishnan and S. Krishnamoorthy, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 2056–2070 CrossRef PubMed
.
- M. Fleischmann, P. J. Hendra and A. J. McQuillan, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1974, 26, 163–166 CrossRef CAS
.
- R. A. Halvorson and P. J. Vikesland, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, 44, 7749–7755 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- L. Qian and X. Yang, Colloids Surf., A, 2005, 260, 79–85 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- H. He, X. Xu, H. Wu and Y. Jin, Adv. Mater., 2012, 24, 1736–1740 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. W. Cao, R. Jin and C. A. Mirkin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 7961–7962 CrossRef CAS
.
- R. Cao, B. Li, Y. Zhang and Z. Zhang, Chem. Commun., 2011, 12301–12303 RSC
.
- J. H. Harwell, J. C. Hoskins, R. S. Schechter and W. H. Wade, Langmuir, 1985, 1, 251–262 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. Wei, L. Wang, Z. Liu, Y. Song, L. Sun, T. Yang and Z. Li, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 23941–23947 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- B. Nikoobakht and M. A. El-Sayed, Langmuir, 2001, 17, 6368–6374 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. M. Alkilany, R. L. Frey, J. L. Ferry and C. J. Murphy, Langmuir, 2008, 24, 10235–10239 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Swami, A. Kumar and M. Sastry, Langmuir, 2003, 19, 1168–1172 CrossRef CAS
.
- F. Hubert, F. Testard and O. Spalla, Langmuir, 2008, 24, 9219–9222 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- B. Baruah, C. Craighead and C. Abolarin, Langmuir, 2012, 28, 15168–15176 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. Ye, L. Jin, H. Caglayan, J. Chen, G. Xing, C. Zheng, V. Doan-Nguyen, Y. Kang, N. Engheta, C. R. Kagan and C. B. Murray, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 2804–2817 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Khan, S. A. Al-Thabaiti, A. Y. Obaid, Z. A. Khan and A. A. O. Al-Youbi, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, 367, 101–108 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- N. C. M. Tam, B. M. T. Scott, D. Voicu, B. C. Wilson and G. Zheng, Bioconjugate Chem., 2010, 21, 2178–2182 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. C. Lee and D. Meisel, J. Phys. Chem., 1982, 86, 3391–3395 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. Laaksonen, P. Ahonen, C. Johans and K. Kontturi, ChemPhysChem, 2006, 7, 2143–2149 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- H. Bar, D. K. Bhui, G. P. Sahoo, P. Sarkar, S. P. De and A. Misra, Colloids Surf., A, 2009, 339, 134–139 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. A. AbdelHamid, M. A. Al-Ghobashy, M. Fawzy, M. B. Mohamed and M. M. S. A. Abdel-Mottaleb, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2013, 1, 1520–1529 CrossRef CAS
.
- X. Bai, X. Li and L. Zheng, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 12209–12214 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. V. Canamares, C. Chenal, R. L. Birke and J. R. Lombardi, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 20295–20300 Search PubMed
.
- E. C. Le Ru, E. Blackie, M. Meyer and P. G. Etchegoin, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 13794–13803 CAS
.
- X. Ling and J. Zhang, Small, 2010, 6, 2020–2025 CrossRef PubMed
.
- A. M. Schwartzberg, C. D. Grant, A. Wolcott, C. E. Talley, T. R. Huser, R. Bogomolni and J. Z. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 19191–19197 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. R. Coon, T. Y. Zakharian, N. L. Littlefield, S. P. Loheide, E. J. Puchkova, R. M. Freeney and V. N. Pak, Langmuir, 2000, 16, 9690–9693 CrossRef CAS
.
- W. Meng, F. Hu, L.-Y. Zhang, X.-H. Jiang, L.-D. Lu and X. Wang, J. Mol. Struct., 2013, 1035, 326–331 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. R. Lombardi and R. L. Birke, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 5605–5617 CAS
.
- S. Nath, S. K. Ghosh, S. Kundu, S. Praharaj, S. Panigrahi and T. Pal, J. Nanopart. Res., 2006, 8, 111–116 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. A. Meyer, E. C. L. Ru and P. G. Etchegoin, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2010, 114, 5515–5519 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- E. Hao, S. Li, R. C. Bailey, S. Zou, G. C. Schatz and J. T. Hupp, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 1224–1229 CrossRef CAS
.
- C.-H. Tsai, J. L. Vivero-Escoto, I. I. Slowing, I. J. Fang, B. G. Trewyn and V. S. Y. Lin, Biomaterials, 2011, 32, 6234–6244 CAS
.
- C. D. Walkey, J. B. Olsen, H. Guo, A. Emili and W. C. W. Chan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 2139–2147 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c4ra09956g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |