Extraction of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) with magnetic albuminoid-imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) nanoparticles from human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cellular culture medium
Abstract
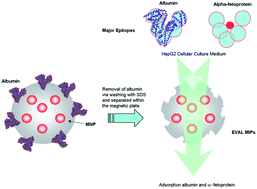
Selective adsorption by magnetic nanoparticles is an effective method for obtaining valuable molecules from biological fluids. The synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymeric composite particles may be utilized routinely to remove a target from a complex mixture (e.g. biological fluids). Nowadays alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is used as an important biomarker in the screening of human hepatocellular carcinoma. The imprinting of albumin (ALB) on poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) based nanoparticles may be adopted for the selective adsorption of AFP, because the two molecules have similar amino acid sequences. In this work, we studied the adsorption of ALB and AFP onto magnetic albuminoid-imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) nanoparticles (i.e. ALB or AFP MMIPs). The binding capacity of the MMIPs increases threefold with imprinting protein concentration (from 0.1 to 1.0 mg mL−1). MMIPs imprinted with 0.5 mg mL−1 of albumin or AFP adsorbed high levels of alpha-fetoprotein (60 ± 6 and 185 ± 17 μg g−1 respectively) from a HepG2 culturing medium diluted by 50×.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...