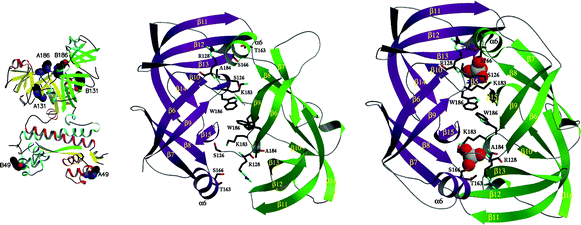
The molybdate-dependent transcriptional regulator ModE of Escherichia coli displays a large (50%) quenching of its intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence on binding molybdate. The changes in fluorescence have been exploited to analyse the binding of molybdate to ModE. Utilising site-directed mutagenesis, a series of phenylalanine substitutions for the three tryptophans of ModE (Trp49, Trp131 and Trp186) have been constructed, to yield three mono-Trp-containing derivatives. This has allowed an assessment to be made of the contribution of each of the three tryptophans to the spectral changes observed on binding molybdate; these are most distinctive for Trp186. Linkage between the DNA-binding and molybdate-binding sites (some 55 Å apart) is shown by (a) the small, but definite, effect of molybdate on the fluorescence of Trp49 which is located at the DNA-binding winged helix–turn–helix domain, and (b) the finding that the binding of either ligand is enhanced in the presence of the other. The studies demonstrate that the mono-Trp derivatives of ModE could be useful tools with which to study the signal transduction processes specifically associated with molybdate-dependent transcriptional regulation and that this approach may have wider implications for analysis of other regulated systems.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...