Dynamic nuclear polarization in a magnetic resonance force microscope experiment†
Abstract
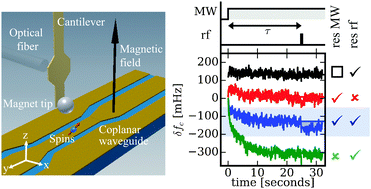
We report achieving enhanced nuclear magnetization in a magnetic resonance force microscope experiment at 0.6 tesla and 4.2 kelvin using the dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) effect. In our experiments a microwire coplanar waveguide delivered radiowaves to excite nuclear spins and microwaves to excite electron spins in a 250 nm thick nitroxide-doped polystyrene sample. Both electron and proton spin resonance were observed as a change in the mechanical resonance frequency of a nearby cantilever having a micron-scale nickel tip. NMR signal, not observable from Curie-law magnetization at 0.6 T, became observable when microwave irradiation was applied to saturate the electron spins. The resulting NMR signal's size, buildup time, dependence on microwave power, and dependence on irradiation frequency was consistent with a transfer of magnetization from electron spins to nuclear spins. Due to the presence of an inhomogeneous magnetic field introduced by the cantilever's magnetic tip, the electron spins in the sample were saturated in a microwave-resonant slice 10's of nm thick. The spatial distribution of the nuclear polarization enhancement factor ε was mapped by varying the frequency of the applied radiowaves. The observed enhancement factor was zero for spins in the center of the resonant slice, was ε = +10 to +20 for spins proximal to the magnet, and was ε = −10 to −20 for spins distal to the magnet. We show that this bipolar nuclear magnetization profile is consistent with cross-effect DNP in a ∼105 T m−1 magnetic field gradient. Potential challenges associated with generating and using DNP-enhanced nuclear magnetization in a nanometer-resolution magnetic resonance imaging experiment are elucidated and discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...