Subwavelength imaging in the visible range using a metal coated carbon nanotube forest†
Abstract
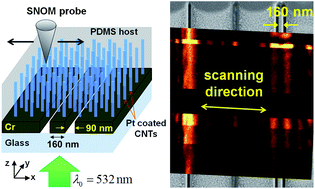
We demonstrate subwavelength imaging in the visible range by using a metal coated carbon nanotube forest. Under 532 nm illumination, a 160 nm separated double slit is resolved. This corresponds to the resolution of 0.3 wavelength. By controlling the growing conditions and with the help of the microtoming technique, we made a dense carbon nanotube forest layer of 400 nm thickness. The metal coated carbon nanotube forest, acting as a wire medium nanolens, delivers imaging information including details in the evanescent fields near the objects.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...