Stability and resistance of nickel catalysts for hydrodeoxygenation: carbon deposition and effects of sulfur, potassium, and chlorine in the feed†
Abstract
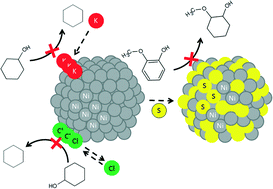
The long term stability and resistance toward carbon deposition, sulfur, chlorine, and potassium of Ni/ZrO2 as a catalyst for the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of guaiacol in 1-octanol (as a model compound system for bio-oil) has been investigated at 250 °C and 100 bar in a trickle bed reactor setup. Without impurities in the feed good stability of the Ni/ZrO2 catalyst could be achieved over more than 100 h of operation, particularly for a sample prepared with small Ni particles, which minimized carbon deposition. Exposing the catalyst to 0.05 wt% sulfur in the feed resulted in rapid deactivation with complete loss of activity due to the formation of nickel sulfide. Exposing Ni/ZrO2 to chlorine-containing compounds (at a concentration of 0.05 wt% Cl) on-stream led to a steady decrease in activity over 40 h of exposure. Removal of the chlorine species from the feed led to the regaining of activity. Analysis of the spent catalyst revealed that the adsorption of chlorine on the catalyst was completely reversible, but chlorine had caused sintering of nickel particles. In two experiments, potassium, as either KCl or KNO3, was impregnated on the catalyst prior to testing. In both cases deactivation was persistent over more than 20 h of testing and severely decreased the deoxygenation activity while the hydrogenation of guaiacol was unaffected. Overall, sulfur was found to be the worst poison, followed by potassium and then chlorine. Thus, removal/limitation of these species from bio-oil is a requirement before long term operation can be achieved with this catalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...