Synthesis and characterization of quantum dots for application in laser soft desorption/ionization mass spectrometry to detect labile metal–drug interactions and their antibacterial activity†
Abstract
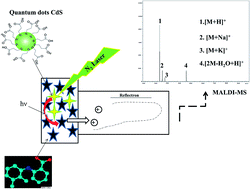
Synthesis and characterization of quantum dot modified mercaptopropionic acid (CdS@MPA) and its application in laser soft desorption/ionization for labile metal–drug interactions is reported. CdS@MPA was synthesised via a hydrothermal method and characterized using TEM, UV-vis absorption, fluorescence, and FTIR spectroscopy. These tiny nanocrystals (<5 nm) provide a large surface area and a UV-vis absorption that is a good match with the N2 laser (337 nm) of matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS). Thus, they softly desorb/ionize labile metallodrugs without destroying the weak noncovalent bonds between the drug and the heavy transition metals (HTMs). Because of the UV absorption at 337 nm and large surface area, the present technique is coined as quantum enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (QELDI-MS). Detection of the interactions of HTMs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in aqueous solution is critical because these coordinations are weak and labile in the acid solution of conventional matrices. QELDI-MS presented a high performance and low limit of detection (0.5 μL, 0.1–0.5 mM) for metallodrug detection in aqueous solution. The antibacterial activities of the metallodrugs against pathogenic bacteria were investigated using optical density (OD600), cell counting and proteomics analysis. Simple detection of the metallodrug in aqueous solution is promising for environmental, biological and analytical concerns.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...