Phosphazenes: efficient organocatalysts for the catalytic hydrosilylation of carbon dioxide†
Abstract
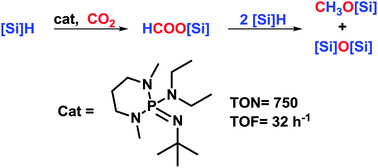
Phosphazene superbases are efficient organocatalysts for the metal-free catalytic hydrosilylation of carbon dioxide. They react with CO2 to form the respective phosphine oxides, but in the presence of hydrosilanes, CO2 can be selectively reduced to silyl formates, which can in turn be reduced to methoxysilanes by addition of an extra loading of silanes. Activities reach a TOF of 32 h−1 with a TON of 759. It is also shown that unexpectedly, N,N-dimethylformamide can reduce CO2 to a mixture of silyl formates, acetals and methoxides in the absence of any catalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...