Tailoring nanorod alignment in a polymer matrix by elongational flow under confinement: simulation, experiments, and surface enhanced Raman scattering application
Abstract
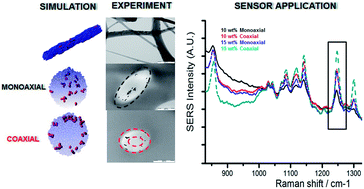
Mesoscale simulation, electrospinning and Raman scattering experiments have been carried out to demonstrate that examination and control of nanorod configuration in a polymer matrix under elongational flow and confinement can lead to enhanced sensing. First, coarse-grained molecular dynamics (CGMD) was employed to probe the diffusivity, orientation, and dispersion of nanorods in a model polymer melt under planar elongational flow. Compared to shear flow, elongational flow gives rise to enhanced dispersion and orientation of nanorods, which are predicted to be improved with increasing the aspect ratio of nanorods and polymer chain length. As comparative experiments, we have electrospun gold (Au) nanorods with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and the resulting Au nanorod configuration in PVA nanofibers is in good agreement with the predicted simulation. Furthermore, coaxial electrospinning of Au nanorod/PVA–PVA (shell–core) was applied to selectively place Au nanorods in the cylindrical sheath layer, and the alignment of Au nanorods near the fiber surface was confirmed by TEM analysis and CGMD simulation under uniaxial elongation. Finally, the Au nanorod–PVA fibers were tested for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for sensing applications. The coaxially electrospun fibers have demonstrated much greater signal peak strength when compared with monoaxially electrospun fibers with the same Au nanorod loading. This comprehensive study demonstrates how extensional flow and multi-layered fluids can direct the orientation and dispersion of nanorod in a polymer matrix, leading to enhanced sensing performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...