Synthesis and properties of a series of quinoxaline-based copolymers: an example to understand the effect of the structure of the mainchain and sidechain on the charge transport ability of the polymers†
Abstract
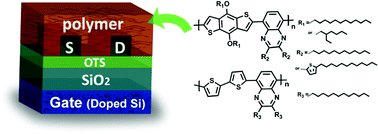
Five D–A (donor–acceptor) copolymers P1–P5 were designed and synthesized, with the mainchain constructed with thiophene derivatives as D and a quinoxaline unit as A, and the sidechain constructed with alkyl groups or alkylthienyl groups. All the polymers showed good thermal stability for device fabrication. The absorption spectra revealed that the five polymers covered a wide absorption range from 300 to 727 nm (with P1), and to 755 nm (with P5). Characterization results showed that both the mainchain and sidechain structures played important roles in the optical, electronic and charge transport properties. OTFT devices were fabricated to evaluate the mobilities of copolymers, and P3 with benzodithiophene and quinoxaline moieties as the mainchain and pure linear alkyl groups as the sidechain manifested the best performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...