Efficient synthesis of acetic acid via Rh catalyzed methanol hydrocarboxylation with CO2 and H2 under milder conditions†
Abstract
Acetic acid is an important bulk chemical and synthesis of acetic acid via methanol hydrocarboxylation with CO2 and H2 is a very promising route. In this work, we studied the reaction over a number of catalytic systems. It was found that Rh2(CO)4Cl2 with 4-methylimidazole (4-MI) as the ligand was very efficient in the presence of LiCl and LiI. Acetic acid began to form at 150 °C. The TOF was as high as 26.2 h−1 and the yield of acetic acid could reach 81.8% at 180 °C. The catalytic system had obvious advantages, such as simplicity, high activity and selectivity, milder reaction conditions, and less corrosiveness. The excellent cooperation of CO and Cl− in Rh2(CO)4Cl2, suitable basicity and aromaticity of the ligand 4-MI, and the hydrogen bonding ability of Cl− were crucial for the outstanding performance of the catalytic system. The control experiments showed that the reaction did not proceed via the CO pathway.
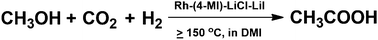


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...