Accelerated catalytic activity of Pd NPs supported on amine-rich silica hollow nanospheres for quinoline hydrogenation†
Abstract
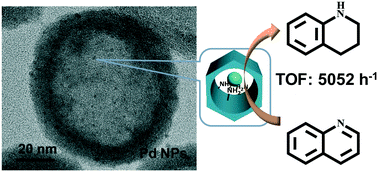
Tuning the catalytic performance of metal nanoparticles (NPs) is very important in nanocatalysis. Herein, we report that amine-rich mesoporous silica hollow nanospheres (HS-NH2) synthesized by one-pot condensation could efficiently stabilize ultra-small Pd NPs and also increase the surface electron density of Pd NPs due to the coordinating and electron-donating effects of the amine group. Pd NPs supported on HS-NH2 afford TOF as high as 5052 h−1 in quinoline hydrogenation reaction and are much more active than Pd/C with a TOF of 960 h−1 as well as most reported solid catalysts. The intrinsic activity of Pd NPs increases as the particle size of Pd decreases, revealing that quinoline hydrogenation is a structure-sensitive reaction. The results of TEM, XPS, CO adsorption and CO stripping voltammetry indicate that the high activity of Pd NPs supported on HS-NH2 is mainly attributed to their ultra-small particle size and high surface electron density. Our primary results demonstrate that the organo-modified silica nanospheres are promising solid supports for modifying the electronic properties of metal NPs supported and consequently tailoring their catalytic functions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Catalysis Science & Technology HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...