Mesoporous semiconducting TiO2 with rich active sites as a remarkable substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering†
Abstract
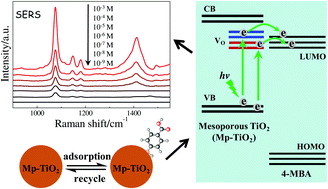
Recently, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) research based on semiconductor TiO2 has received increasing attention. However, the practical application of TiO2 SERS-active substrates has been hampered due to their lower surface performance and detection sensitivity. Here we report a new strategy to enhance the SERS activity of TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) by means of formation of a mesoporous framework via reductive calcination of polymer coated nanocrystals. The 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) probe molecules on the mesoporous TiO2 substrate exhibit larger SERS enhancement compared with that on the ordinary TiO2 NP substrate; this considerable SERS enhancement mainly stems from the contributions of rich surface active sites of mesoporous TiO2, which can provide more effective adsorption sites for the molecules and promote the charge transfer between the substrate and the adsorbed molecule, and thus remarkably enhance SERS signals. On the mesoporous TiO2, a detection limit of 4-MBA as low as 1 × 10−8 mol L−1 can be achieved, which is the highest sensitivity among those reported for semiconducting substrates and even comparable with those of noble metal substrates. And, it is proved that the mesoporous TiO2 substrates are characterized by high stability and self-cleaning properties, and can be repeatedly used in SERS detection without losing their activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...